Introduction to Dairy-Free Yogurt
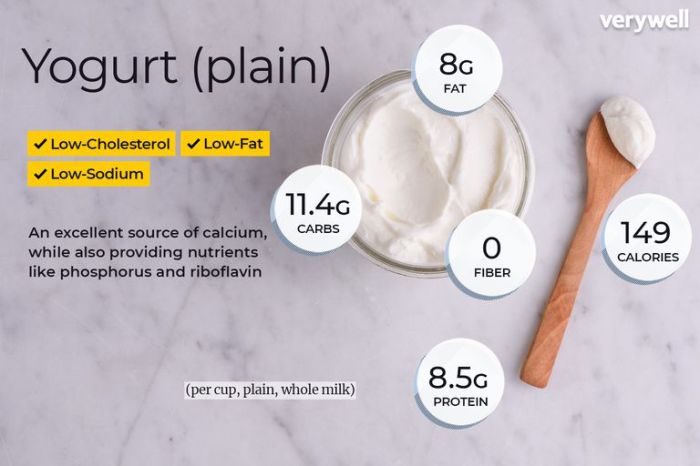
So delicious dairy-free yogurt nutrition facts – The dairy-free yogurt market is experiencing significant growth, driven by increasing consumer demand for plant-based alternatives. This surge in popularity reflects broader trends towards healthier eating habits, ethical concerns about dairy farming, and the rising prevalence of lactose intolerance and other dairy allergies. Dairy-free yogurts offer a delicious and nutritious option for individuals seeking to exclude dairy from their diets, while still enjoying the creamy texture and probiotic benefits associated with traditional yogurt.The increasing popularity of dairy-free yogurt stems from several key factors.
Firstly, a growing awareness of the health benefits of plant-based diets is influencing consumer choices. Secondly, many individuals experience digestive discomfort or allergic reactions to dairy products, leading them to seek suitable alternatives. Thirdly, ethical concerns regarding the environmental impact and animal welfare practices within the dairy industry are prompting consumers to explore plant-based options.
Finally, the increasing availability and improved taste of dairy-free yogurts have made them a more appealing and accessible choice.
Types of Dairy-Free Yogurt
Dairy-free yogurts are available in a wide variety of options, each offering a unique flavor profile and nutritional composition. These variations cater to diverse preferences and dietary needs. Popular examples include almond yogurt, known for its subtly sweet and nutty flavor; soy yogurt, offering a creamy texture and a higher protein content compared to some other alternatives; and coconut yogurt, characterized by its rich, creamy texture and slightly sweet taste.
Other options include cashew, oat, and even pea-protein based yogurts, each with its own distinct characteristics. The diversity in the market ensures there’s a dairy-free yogurt to suit almost every palate.
Nutritional Comparison of Dairy and Dairy-Free Yogurts
Dairy and dairy-free yogurts offer a range of nutritional profiles, catering to diverse dietary needs and preferences. Understanding these differences is crucial for making informed choices about your diet. This comparison focuses on macronutrients – protein, fat, and carbohydrates – highlighting key similarities and disparities across various options.
Macronutrient Profiles of Dairy and Dairy-Free Yogurts
The following table provides a general comparison of macronutrient content. Note that specific values vary significantly depending on brand, flavor, and added ingredients. These are average values for a standard serving size (approximately 170g).
| Yogurt Type | Protein (grams) | Fat (grams) | Carbohydrates (grams) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dairy Yogurt (Plain, Full-Fat) | 10-15 | 8-10 | 10-15 |
| Dairy Yogurt (Plain, Low-Fat) | 10-12 | 0-2 | 12-17 |
| Almond Yogurt (Plain, Unsweetened) | 2-5 | 4-7 | 5-10 |
| Soy Yogurt (Plain, Unsweetened) | 7-10 | 2-5 | 10-15 |
| Coconut Yogurt (Plain, Unsweetened) | 2-4 | 5-8 | 10-15 |
Nutritional Differences Among Dairy-Free Yogurt Bases
Almond yogurt is generally lower in protein and carbohydrates than dairy yogurt but can be comparable in fat content, depending on the brand. Soy yogurt provides a good source of protein, often closer to dairy yogurt in this respect, with moderate fat and carbohydrate levels. Coconut yogurt is usually lower in protein than both dairy and soy yogurts, with a higher fat content and a similar carbohydrate range to dairy and soy options.
The specific nutritional content of each type is influenced by factors like the type of nut or seed milk used, added sugars, and other ingredients.
Health Benefits and Drawbacks of Dairy-Free Yogurts
Dairy-free yogurts offer several potential benefits, such as being suitable for individuals with lactose intolerance or dairy allergies. Soy yogurt, in particular, can be a good source of plant-based protein. However, some dairy-free options may be lower in protein and calcium compared to dairy yogurt. Furthermore, many commercially available dairy-free yogurts contain added sugars, which should be considered when making dietary choices.
The high fat content in some coconut and almond yogurts should also be factored into overall dietary considerations. Always check the nutrition label for a complete picture of the nutritional content.
Impact of Processing on Nutritional Content: So Delicious Dairy-free Yogurt Nutrition Facts
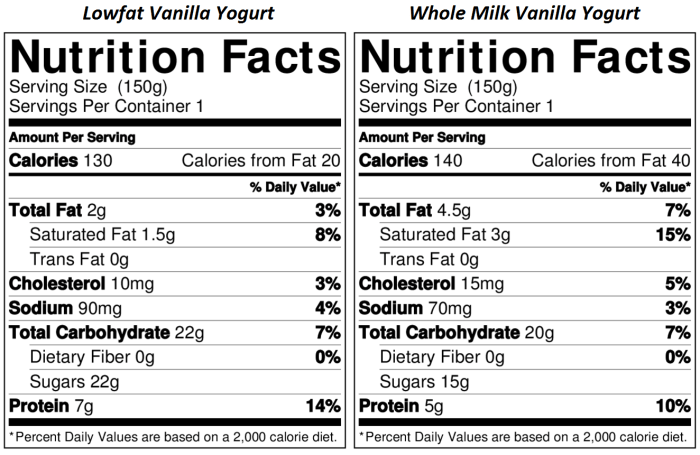
Dairy-free yogurt undergoes various processing steps that can significantly influence its final nutritional profile. Understanding these processes is crucial for making informed choices about which products best meet individual dietary needs. Factors like heat treatment and fermentation impact the levels of vitamins, minerals, and beneficial compounds.Processing methods employed in the production of dairy-free yogurts can alter the nutritional value of the final product.
While some processes aim to enhance safety and shelf life, others may inadvertently reduce the concentration of certain beneficial nutrients. Let’s examine the effects of common processing methods.
Effects of Pasteurization and Fermentation
Pasteurization, a heat treatment process, eliminates harmful bacteria, extending the shelf life of the yogurt. However, high temperatures can degrade heat-sensitive vitamins like vitamin C and certain B vitamins. Fermentation, on the other hand, is a crucial step in dairy-free yogurt production. It involves the use of beneficial bacteria that convert sugars into lactic acid, giving yogurt its characteristic tangy flavor and improving digestibility.
This process can also increase the bioavailability of certain nutrients and create beneficial compounds like probiotics. The type and strain of bacteria used in fermentation can further influence the final nutritional composition.
| Processing Method | Effect on Key Nutrients |
|---|---|
| Pasteurization (High-Heat) | Reduces levels of heat-sensitive vitamins (e.g., vitamin C, some B vitamins); may slightly reduce enzyme activity. |
| Pasteurization (Low-Heat/Ultra-High Temperature) | Minimizes vitamin loss compared to high-heat pasteurization; may still slightly affect enzyme activity. |
| Fermentation | Increases bioavailability of some nutrients; produces beneficial compounds (probiotics); may slightly reduce some sugars. |
| Homogenization | Creates a smoother texture; may slightly reduce the bioavailability of some nutrients due to changes in fat particle size. |
Nutritional Comparison: Raw vs. Processed Dairy-Free Yogurt, So delicious dairy-free yogurt nutrition facts
While raw dairy-free yogurt might offer a higher concentration of certain heat-sensitive nutrients, the risk of harmful bacteria makes its consumption potentially unsafe. Processed dairy-free yogurt, having undergone pasteurization, is significantly safer for consumption. The trade-off is a potential reduction in some nutrients due to the heat treatment. Therefore, consumers must weigh the benefits of enhanced safety against the potential reduction in certain nutrient levels.
For example, a raw almond yogurt might contain slightly higher levels of vitamin E than its pasteurized counterpart, but the pasteurized version would be free from the risk of harmful bacteria. This illustrates the critical balance between safety and nutrient retention in dairy-free yogurt production.
Dairy-Free Yogurt and Dietary Needs

Dairy-free yogurt offers a delicious and nutritious alternative for individuals with various dietary restrictions and preferences. Its versatility makes it a valuable addition to balanced diets across different age groups and activity levels, providing essential nutrients while accommodating specific needs.Dairy-free yogurt’s suitability is largely determined by its ingredients and the individual’s dietary requirements.
Dairy-Free Yogurt for Specific Dietary Needs
Choosing the right dairy-free yogurt depends on individual dietary needs. For example, individuals with lactose intolerance can safely consume any dairy-free option, as these yogurts are naturally lactose-free. Vegans will need to select yogurts made without any animal products, ensuring the ingredients list excludes honey, whey, or casein. People with allergies must carefully check labels for potential allergens, such as nuts, soy, or coconut, depending on their specific sensitivities.
Many dairy-free yogurts are fortified with vitamins and minerals, often including calcium and vitamin D, which are commonly found in dairy yogurt. This fortification helps ensure nutritional adequacy for those avoiding dairy.
Incorporating Dairy-Free Yogurt into Balanced Diets
Dairy-free yogurt seamlessly integrates into balanced diets for various demographics. For children, it provides a good source of calcium and protein for healthy growth and development. The creamy texture makes it appealing for young eaters, and it can be easily incorporated into smoothies or used as a base for healthy snacks. Active adults can benefit from the protein content, which aids muscle recovery and repair.
Older adults may appreciate the calcium and vitamin D content, which are essential for maintaining bone health. Portion sizes should be adjusted based on individual caloric needs and activity levels. For example, a smaller portion might be suitable for a sedentary older adult compared to an active young adult.
Dairy-Free Yogurt Recipes
Dairy-free yogurt’s versatility shines through in its culinary applications. It can be a breakfast staple, a midday snack, or a component in savory dishes.
Breakfast: A simple and nutritious breakfast bowl can be made with dairy-free yogurt, topped with granola, berries, and a drizzle of honey or maple syrup (depending on dietary needs). A quick smoothie incorporating dairy-free yogurt, frozen fruit, and spinach provides a healthy and refreshing start to the day.
Snack: Dairy-free yogurt with chopped fruit and nuts makes a satisfying and portable snack. It can also be used as a dip for fruits and vegetables.
Savory Dishes: Dairy-free yogurt can be used as a substitute for sour cream or cream cheese in dips, sauces, and dressings. It adds a creamy texture and tangy flavor to various dishes, such as tzatziki sauce or creamy pasta sauces.
Example Recipe: Mango Lassi (Vegan): Blend 1 cup of mango chunks, ½ cup of coconut yogurt, ¼ cup of water, and a pinch of cardamom. This provides a refreshing and naturally sweet beverage rich in vitamins and probiotics.
So Delicious dairy-free yogurt offers a compelling nutritional profile, particularly for those seeking plant-based alternatives. For comparison, you might find it interesting to review the nutritional information of other healthy options like bone broth, readily available by checking out the detailed kettle and fire nutrition facts to understand macronutrient differences. Returning to So Delicious, its lower fat content and higher protein options make it a versatile choice for various dietary needs.
Consumer Perception and Market Trends
The dairy-free yogurt market is experiencing significant growth, driven by increasing consumer demand for plant-based alternatives and a heightened awareness of health and sustainability. Understanding consumer perceptions and purchasing habits is crucial for manufacturers to effectively navigate this dynamic landscape. This section explores key trends shaping the future of dairy-free yogurt.
Market research consistently reveals a rising preference for dairy-free options among consumers. This shift is influenced by several factors, including lactose intolerance, ethical concerns regarding animal welfare, and the growing popularity of vegan and vegetarian lifestyles. Furthermore, many consumers perceive dairy-free yogurts as healthier alternatives, associating them with reduced fat, cholesterol, and potential allergy benefits. However, it’s important to note that not all dairy-free yogurts are created equal in terms of nutritional profile.
Consumer Preferences and Purchasing Habits
Data from market research firms like Nielsen and Mintel indicates a strong preference for certain flavors and functionalities within the dairy-free yogurt sector. Plain and vanilla remain popular choices, mirroring trends in the traditional yogurt market. However, innovative flavor profiles such as mango, coconut, and various berry blends are driving growth, catering to evolving consumer palates. Additionally, the demand for yogurts with added probiotics, protein, and other functional ingredients is steadily increasing.
For example, a significant portion of consumers are actively seeking high-protein dairy-free yogurts to support fitness goals, while others prioritize yogurts with added prebiotics for gut health benefits.
Emerging Trends in the Dairy-Free Yogurt Market
The dairy-free yogurt market is characterized by continuous innovation. Beyond novel flavor combinations, we see a rise in functional dairy-free yogurts incorporating ingredients like collagen peptides for skin health, adaptogens for stress management, and various superfoods for enhanced nutritional value. For instance, the inclusion of ingredients like turmeric or spirulina is becoming increasingly common, reflecting consumer interest in functional foods that offer health benefits beyond basic nutrition.
Furthermore, the market is witnessing a growing emphasis on sustainability, with brands highlighting eco-friendly packaging and sourcing practices to attract environmentally conscious consumers.
Future Directions of the Dairy-Free Yogurt Industry
The future of the dairy-free yogurt industry appears bright, with projections indicating continued expansion. We can expect to see further diversification in terms of both base ingredients (beyond soy, almond, and coconut) and functional additions. The development of new plant-based proteins, such as pea protein or fava bean protein, might lead to the creation of dairy-free yogurts with improved texture and nutritional profiles.
Furthermore, the industry is likely to focus on addressing challenges related to cost and sustainability, potentially through advancements in production processes and ingredient sourcing. The development of more sophisticated and cost-effective technologies for creating dairy-free yogurt with a texture and taste that closely resembles traditional yogurt will also be a key area of focus. For example, companies are actively investing in research to improve the creaminess and mouthfeel of plant-based yogurts, a factor that influences consumer acceptance.
FAQ Guide
What are the common allergens found in dairy-free yogurts?
Common allergens vary depending on the base ingredient. Soy, almond, and coconut are frequent sources of allergic reactions. Always check the label for a complete list of ingredients and potential allergens.
How does the shelf life of dairy-free yogurt compare to traditional yogurt?
Shelf life varies depending on the brand and preservation methods used. Generally, dairy-free yogurts have a comparable or slightly shorter shelf life than traditional yogurt due to their different composition and processing.
Are all dairy-free yogurts suitable for individuals with specific dietary restrictions (e.g., gluten-free)?
Not necessarily. While many are naturally gluten-free, some may contain added ingredients that contain gluten. Always check the label for gluten-free certification or a complete ingredient list.
Can dairy-free yogurt be frozen?
Freezing dairy-free yogurt may alter its texture, resulting in a potentially icy or grainy consistency upon thawing. While possible, it’s generally not recommended for optimal taste and texture.

