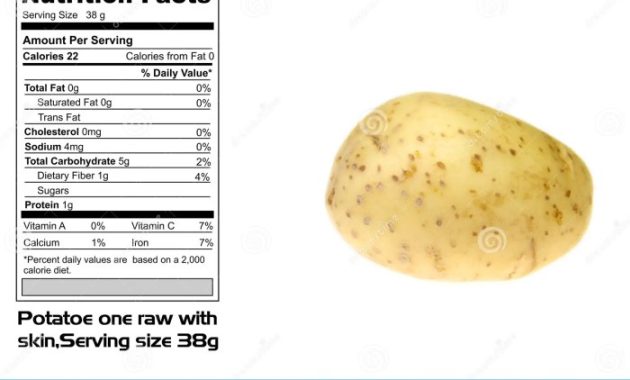
Potatoes in a Balanced Diet

Nutrition facts on potatoes – Potatoes, often unfairly maligned, can be a valuable component of a healthy and balanced diet when consumed thoughtfully. Their nutritional profile, encompassing carbohydrates, vitamins, and minerals, contributes significantly to overall well-being, provided portion sizes are managed effectively. Understanding how to incorporate potatoes into different dietary plans is key to maximizing their benefits.
Yo, so you’re checking potato nutrition facts, right? Like, how many carbs are in a baked spud? But if you’re looking for a sweeter, more convenient snack with a different nutritional profile, check out the juice plus gummies nutrition facts – they’re pretty lit. Then, compare that to your potato stats – it’s all about balance, fam.
Potatoes are cool, but variety is the spice of life, you know?
A Sample Meal Plan Incorporating Potatoes
A balanced diet includes a variety of food groups, and potatoes can easily fit into this framework. The following sample meal plan demonstrates how potatoes can be part of a healthy eating pattern, showcasing their versatility.
- Breakfast: A small baked potato topped with a poached egg and a sprinkle of chives. This provides protein, healthy fats, and complex carbohydrates for sustained energy.
- Lunch: A hearty potato and vegetable soup, incorporating other nutritious vegetables like carrots, celery, and peas. This offers a balanced mix of nutrients and fiber.
- Dinner: Roasted chicken breast with roasted sweet potatoes and a side of steamed broccoli. This meal provides lean protein, complex carbohydrates, and essential vitamins.
The Nutritional Role of Potatoes
Potatoes are a good source of carbohydrates, providing the body with essential energy. They also contain vitamin C, potassium, and fiber. The type of potato and cooking method can influence the nutritional content; for example, leaving the skin on retains more fiber and nutrients. A medium-sized baked potato with the skin on provides approximately 160 calories, 4 grams of fiber, and a significant portion of the daily recommended intake of vitamin C and potassium.
This energy contribution is vital for physical activity and overall bodily functions.
Incorporating Potatoes into Various Diets
Potatoes can be adapted to suit various dietary needs. In vegetarian and vegan diets, potatoes serve as a good source of carbohydrates and can be included in a variety of dishes, such as potato curry, potato and lentil stew, or as a side dish alongside other vegetables and legumes. For those following a low-carb diet, portion control is crucial.
Smaller portions of potatoes, particularly those prepared without added fats, can still be enjoyed as part of a balanced low-carb meal plan. Sweet potatoes, due to their slightly lower glycemic index compared to white potatoes, may be preferred in such diets.
Portion Control and Nutritional Impact
Portion control significantly influences the nutritional impact of potato consumption. While potatoes offer essential nutrients, consuming excessive amounts can lead to increased calorie intake. A standard serving size of a medium-sized potato (approximately 5-6 inches in diameter) is a reasonable portion for most adults. Larger portions should be avoided to prevent unnecessary calorie consumption and potential weight gain.
Choosing cooking methods that minimize added fats, such as baking, boiling, or steaming, further contributes to a healthier dietary approach.
Potential Health Effects of Potato Consumption
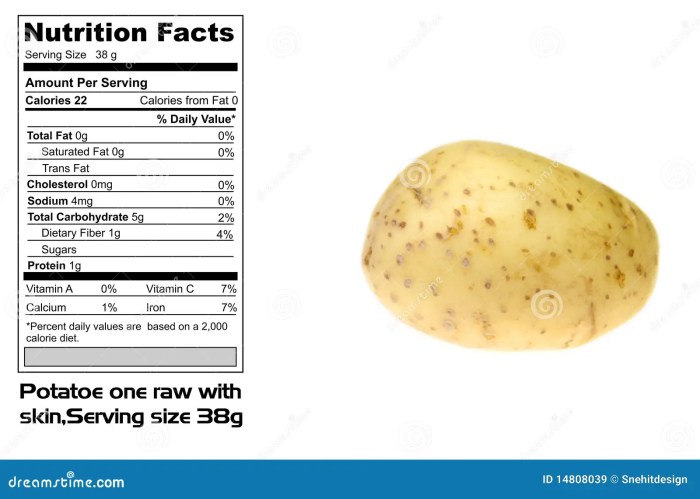
Potatoes, a staple food in many cultures, offer a range of nutritional benefits and potential drawbacks depending on consumption patterns and preparation methods. Understanding these effects is crucial for incorporating potatoes into a healthy and balanced diet.Potatoes are a good source of several essential nutrients. Their contribution to overall health is complex and depends on various factors.
Benefits of Potato Consumption
The nutritional profile of potatoes includes significant amounts of potassium, a vital electrolyte crucial for maintaining healthy blood pressure. Furthermore, potatoes’ high fiber content contributes to improved satiety, aiding in weight management by promoting feelings of fullness and reducing overall calorie intake. The vitamin C content also supports the immune system. For example, a medium-sized baked potato provides a significant portion of the recommended daily intake of vitamin C and potassium.
Drawbacks of Excessive Potato Consumption
Excessive potato consumption, particularly of fried or processed varieties, can negatively impact health. Potatoes possess a relatively high glycemic index (GI), meaning they can cause rapid spikes in blood sugar levels. This is especially concerning for individuals with diabetes or those at risk of developing the condition. Furthermore, the high carbohydrate content, when combined with high-fat preparation methods, can contribute to weight gain if calorie intake exceeds expenditure.
For instance, a large serving of French fries provides a substantial amount of calories and fat, significantly impacting daily energy balance.
Potato Consumption and Health Conditions, Nutrition facts on potatoes
The relationship between potato consumption and various health conditions is multifaceted. High glycemic index potatoes can exacerbate blood sugar control in individuals with diabetes, requiring careful portion control and mindful preparation methods. However, the potassium content in potatoes can contribute positively to cardiovascular health by helping regulate blood pressure, potentially reducing the risk of heart disease. The impact on cholesterol levels is less clear-cut and depends largely on other dietary factors and preparation methods.
Studies have shown conflicting results, highlighting the importance of considering overall dietary patterns rather than focusing solely on potato consumption.
Recommendations for Healthy Potato Consumption
Choosing healthy preparation methods is crucial. The following recommendations promote the benefits and minimize the potential drawbacks of potato consumption:
- Choose baking, boiling, or steaming over frying.
- Consume potatoes in moderation as part of a balanced diet.
- Opt for whole potatoes rather than processed potato products.
- Pair potatoes with sources of protein and healthy fats to moderate their glycemic impact.
- Consider incorporating potatoes into meals strategically, paying attention to portion sizes and overall calorie intake.
Helpful Answers: Nutrition Facts On Potatoes
Are all potatoes created equal nutritionally?
No, different potato varieties (russet, red, sweet) have varying nutrient profiles. Sweet potatoes, for example, are significantly higher in Vitamin A.
Do potatoes cause weight gain?
Excessive consumption of potatoes, especially fried ones, can contribute to weight gain due to high calorie and carbohydrate content. Portion control is key.
Are potatoes good for diabetics?
Potatoes have a relatively high glycemic index. Diabetics should consume them in moderation and choose preparation methods that minimize the glycemic impact (e.g., baked rather than fried).
Can I eat potatoes on a low-carb diet?
While potatoes are a carbohydrate source, they can be included in moderation in some low-carb diets. Consider smaller portions and choose low-starch varieties.